When it comes to coffee, there’s often a lot of confusion about what has more caffeine and what doesn’t. One question that pops up quite a bit is, “do espresso beans have caffeine?” Spoiler alert: Yes, they do! But let’s break it down and explore this topic in detail.
Espresso is a beloved beverage, known for its rich flavor and potent kick. The magic behind that shot of espresso lies in the beans themselves. But what exactly are espresso beans, and how much caffeine do they really pack? In this article, we’re going to answer the burning question: “do espresso beans have caffeine?” We’ll also delve into the nuances of caffeine content in espresso compared to other types of coffee. So, grab your favorite cup of joe, and let’s get started on this caffeinated journey!

Understanding Espresso Beans
Espresso beans are essentially coffee beans, but they’re treated a bit differently. The term “espresso” doesn’t refer to a specific type of coffee bean but rather to the brewing method. However, certain beans are often labeled as “espresso beans” because they are roasted and blended to complement this brewing process.

How Do Espresso Beans Differ from Regular Coffee Beans?
- Roasting Process:
- Espresso Beans: Typically roasted for a longer time to a darker level. This brings out a bold, rich flavor with less acidity.
- Regular Coffee Beans: Can be roasted to various levels (light, medium, dark) depending on the desired flavor profile. Light roasts are more acidic, while dark roasts are more robust.
- Grind Size:
- Espresso Beans: Ground much finer than regular coffee beans. The fine grind is essential for creating the intense pressure needed to brew a proper espresso shot.
- Regular Coffee Beans: The grind size can vary from coarse (for French press) to medium (for drip coffee makers).
- Brewing Method:
- Espresso: Uses high pressure and a short brewing time (about 25-30 seconds) to extract a concentrated shot of coffee.
- Regular Coffee: Usually brewed using gravity, with a longer brewing time, resulting in a less concentrated coffee.
Unique Characteristics of Espresso Beans
- Flavor Profile: Espresso beans, due to their darker roast, have a deep, rich, and sometimes slightly bitter taste. This makes them perfect for creating that signature espresso flavor.
- Oil Content: Darker roasted beans tend to have more surface oils, contributing to the crema (the creamy, golden layer on top of an espresso shot).
- Caffeine Content: Despite common misconceptions, the caffeine content in espresso beans is not necessarily higher than in regular coffee beans. However, the brewing method and concentration make a shot of espresso seem more potent.

The Roasting Process and Its Impact on Caffeine Levels
Roasting is a crucial step in transforming green coffee beans into the aromatic delights we know and love. But how does this process impact the caffeine levels in espresso beans? Let’s break it down by comparing light, medium, and dark roasts.

Light Roast
- Characteristics: Light roast beans are roasted for the shortest amount of time, just until the first crack occurs. They retain most of the original flavors of the coffee bean, often described as bright, fruity, and acidic.
- Caffeine Content: Contrary to popular belief, light roast beans actually have slightly more caffeine than darker roasts. This is because the beans retain more of their original mass, and thus more caffeine, due to the shorter roasting time.
Medium Roast
- Characteristics: Medium roast beans are roasted a bit longer than light roasts, up to just before the second crack. They have a balanced flavor profile, combining the brightness of light roasts with the deeper flavors of dark roasts.
- Caffeine Content: Medium roasts have a slightly lower caffeine content compared to light roasts but still pack a decent punch. They strike a balance, maintaining some of the original caffeine content while developing a richer flavor.
Dark Roast
- Characteristics: Dark roast beans are roasted the longest, past the second crack. They have a deep, rich flavor with low acidity and a pronounced bitterness. The surface of the beans often appears oily due to the extended roasting.
- Caffeine Content: Dark roast beans have the lowest caffeine content of the three roast levels. The prolonged exposure to heat causes a reduction in the bean’s mass, slightly diminishing its caffeine content. However, the robust flavor can make it seem like it has more caffeine.
When it comes to espresso, the roast level plays a significant role in the flavor profile and perceived strength. Espresso beans are typically dark roasted to achieve a bold and intense flavor. While dark roasts have slightly less caffeine per bean compared to lighter roasts, the concentrated brewing process of espresso often delivers a strong caffeine kick.
Caffeine Content in Espresso vs. Regular Coffee
When it comes to caffeine, not all coffee drinks are created equal. Let’s dive into the details and compare the caffeine content in espresso versus regular coffee, taking into account serving sizes and their effects.

Serving Sizes Matter
Before we compare caffeine content, it’s essential to understand that serving sizes play a significant role:
- Espresso: Typically served as a single shot (about 1 ounce or 30 milliliters).
- Regular Coffee: Usually served in an 8-ounce cup (about 240 milliliters).
Caffeine Content per Serving
- Espresso:
- A single shot of espresso contains approximately 63 milligrams of caffeine.
- Double shots, which are common in many coffee drinks, contain about 125 milligrams of caffeine.
- Regular Coffee:
- An 8-ounce cup of regular drip coffee contains roughly 95 milligrams of caffeine.
- This amount can vary widely depending on the coffee bean type, brewing method, and strength of the brew.
Concentration and Perception
- Concentration: Espresso is much more concentrated than regular coffee. With about 63 milligrams of caffeine packed into just 1 ounce, espresso delivers a potent jolt in a small volume.
- Perception: Because espresso is consumed quickly due to its small serving size, it can give the impression of a stronger caffeine kick. In contrast, regular coffee is sipped over a more extended period, leading to a slower, more gradual caffeine intake.
How Much Caffeine is in Your Espresso Shot?
Espresso shots are small but mighty when it comes to caffeine content. Let’s get into the specifics of how much caffeine is in a typical shot of espresso and the factors that can influence it.

Typical Caffeine Content
A standard single shot of espresso (about 1 ounce or 30 milliliters) contains approximately 63 milligrams of caffeine. This amount can vary slightly depending on several factors, which we’ll explore below.
Factors Influencing Caffeine Content
- Coffee Bean Type:
- Arabica vs. Robusta: Arabica beans generally have less caffeine compared to Robusta beans. An espresso made with Robusta beans can have a higher caffeine content.
- Roast Level:
- Light vs. Dark Roasts: As discussed earlier, light roast beans have slightly more caffeine than dark roast beans. However, espresso is typically made with dark roast beans, which have a bold flavor but slightly less caffeine per bean.
- Grinding Size:
- The fineness of the grind affects the caffeine extraction. Finer grinds, typical for espresso, can lead to more efficient caffeine extraction.
- Brewing Time and Pressure:
- Time: The standard brewing time for an espresso shot is around 25-30 seconds. Longer brewing times can extract more caffeine but might also result in over-extraction, affecting the taste.
- Pressure: The high pressure used in espresso machines (around 9 bars) helps extract caffeine quickly and efficiently.
- Dose:
- The amount of coffee used in making the espresso shot can influence caffeine content. A standard shot uses about 7-9 grams of coffee, but variations in dosing can lead to slight differences in caffeine levels.
- Serving Size:
- Ristretto: A shorter, more concentrated shot with less water, resulting in slightly less caffeine due to the reduced volume.
- Lungo: A longer shot with more water, which can extract more caffeine but also dilute the overall concentration.
Practical Example: Let’s consider a typical scenario to illustrate:
- Single Shot: About 7-9 grams of dark roast Arabica beans, brewed for 25-30 seconds under high pressure, yields approximately 63 milligrams of caffeine.
- Double Shot: Doubling the dose to 14-18 grams results in about 125 milligrams of caffeine, making it a favorite for those needing a stronger kick.

Knowing how much caffeine in an espresso shot can vary depending on various elements. When it comes to caffeine in 3 espresso shots, things get interesting. Consuming three standard shots, each containing approximately 63 milligrams of caffeine, sums up to around 189 milligrams in total. That’s enough to give you a significant boost in alertness and focus, but remember, moderation is key to enjoying your espresso experience without overdoing it on caffeine.
Health Effects of Caffeine from Espresso
Caffeine, especially in the concentrated form found in espresso, can have various effects on the body. Let’s explore the health implications of consuming caffeine from espresso, looking at both the benefits and potential risks.
Benefits of Caffeine from Espresso
- Increased Alertness and Focus:
- Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, leading to improved mental alertness and concentration. A shot of espresso can provide a quick and efficient way to boost your cognitive functions, especially during those sluggish mornings or mid-afternoon slumps.
- Enhanced Physical Performance:
- Caffeine is known to enhance physical performance by increasing adrenaline levels, which can improve endurance and strength. This makes espresso a popular pre-workout choice for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
- Mood Improvement:
- Regular, moderate caffeine consumption has been linked to reduced risk of depression and improved mood. The quick jolt of energy from an espresso shot can also provide an immediate mood lift.
- Antioxidant Properties:
- Coffee, including espresso, is rich in antioxidants, which help combat free radicals in the body. These antioxidants can reduce inflammation and lower the risk of certain chronic diseases, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolism Boost:
- Caffeine can increase your metabolic rate, aiding in weight management. An espresso shot can slightly boost your metabolism, helping you burn calories more efficiently.
Potential Risks of Caffeine from Espresso
- Sleep Disturbances:
- Consuming caffeine too close to bedtime can interfere with sleep quality and duration. The stimulating effects of caffeine can keep you awake longer, leading to insomnia or restless nights.
- Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure:
- Caffeine can cause a temporary increase in heart rate and blood pressure, which may be concerning for individuals with cardiovascular conditions. It’s essential to monitor your intake if you have pre-existing heart issues.
- Dependency and Withdrawal:
- Regular consumption of caffeine can lead to physical dependence. Abruptly stopping caffeine intake can result in withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, irritability, and fatigue.
- Digestive Issues:
- Caffeine can stimulate the production of stomach acid, which may lead to digestive issues such as acid reflux or upset stomach. Drinking espresso on an empty stomach can exacerbate these effects.
- Anxiety and Jitters:
- High doses of caffeine can increase anxiety levels and cause jitters or nervousness. Individuals sensitive to caffeine might experience these symptoms even with a single shot of espresso.
Balancing Benefits and Risks: To enjoy the benefits of caffeine from espresso while minimizing the risks, consider the following tips:
- Moderation: Limit your espresso intake to 1-2 shots per day to avoid excessive caffeine consumption.
- Timing: Avoid consuming espresso in the late afternoon or evening to prevent sleep disturbances.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body reacts to caffeine and adjust your intake accordingly.
Safe Caffeine Consumption Levels
Understanding safe caffeine consumption levels is crucial for maintaining health and well-being. Let’s explore the guidelines and recommendations from health authorities to ensure you’re enjoying your espresso safely.

Recommended Daily Caffeine Intake
Health authorities provide clear guidelines on how much caffeine is considered safe for most adults:
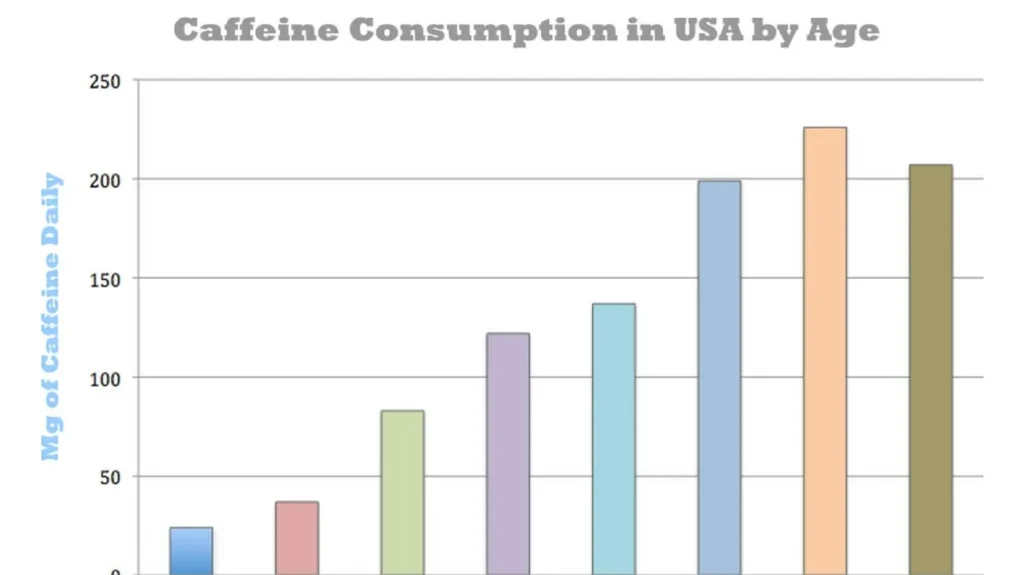
- General Recommendations:
- The FDA suggests that up to 400 milligrams of caffeine per day is generally safe for most healthy adults. This is roughly equivalent to about 4-5 cups of coffee or 6-7 shots of espresso.
- Specific Populations:
- Pregnant Women: The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that pregnant women limit their caffeine intake to 200 milligrams per day, about 2 cups of coffee.
- Adolescents and Children: The American Academy of Pediatrics advises that children and adolescents should avoid caffeine, or at least limit intake to 100 milligrams per day, which is about one cup of coffee.
Practical Tips for Safe Caffeine Consumption
- Monitor Intake: Keep track of your daily caffeine intake from all sources, including coffee, tea, energy drinks, and even foods like chocolate.
- Timing Matters: Avoid consuming caffeine late in the day to prevent sleep disturbances. Aim to have your last caffeinated drink at least 6 hours before bedtime.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body reacts to caffeine. If you experience symptoms like rapid heartbeat, anxiety, or insomnia, consider reducing your intake.
- Stay Hydrated: Caffeine is a diuretic, meaning it can lead to increased urination and dehydration. Ensure you drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
FAQs on Espresso Beans and Caffeine
Curiosity about espresso beans and their caffeine content often leads to many questions. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones to enhance your understanding and engagement with this delightful beverage.
Yes, you can eat espresso beans, and they are often enjoyed covered in chocolate. Eating espresso beans provides a concentrated caffeine boost. On average, a single chocolate-covered espresso bean contains about 1-3 milligrams of caffeine.
A single chocolate-covered espresso bean contains roughly 1-3 milligrams of caffeine, depending on the size of the bean, the type of coffee bean, and the thickness of the chocolate coating. Eating 10 beans would give you about 10-30 milligrams of caffeine.
Yes, decaf espresso still contains a small amount of caffeine. A typical shot of decaf espresso has about 2-5 milligrams of caffeine, significantly less than regular espresso but not completely caffeine-free.
Conclusion
We’ve journeyed through the world of espresso beans and caffeine, uncovering fascinating details and practical insights. Let’s wrap up by summarizing the key points and offering best practices for enjoying espresso in a healthy way.
Summary of Key Points
Espresso Beans and Caffeine:
- Espresso beans are roasted and ground for espresso brewing.
- Espresso has a higher caffeine concentration per ounce than regular coffee.
Roasting and Caffeine Content:
- Light roasts have more caffeine, but espresso uses dark roasts for flavor.
- Caffeine in espresso depends on bean type, roast, grind, brewing time, and pressure.
Espresso vs. Regular Coffee:
- One shot of espresso has ~63 mg of caffeine; an 8 oz coffee has ~95 mg.
- Espresso delivers caffeine quickly; regular coffee releases it gradually.
Health Effects of Caffeine:
- Benefits: increased alertness, performance, mood, antioxidants.
- Risks: sleep issues, heart rate increase, dependency, digestive problems, anxiety.
Safe Caffeine Consumption:
- Up to 400 mg of caffeine/day is safe for most adults (about 6-7 espresso shots).
- Pregnant women and some health conditions require lower caffeine intake.
Disclosure: Our blog contains affiliate links to products. We may receive a commission for purchases made through these links. However, this does not impact our reviews and comparisons. We try our best to keep things fair and balanced, in order to help you make the best choice for you.



2 Responses